Introduction
In CNC machining, spindle runout is crucial to machining accuracy and quality. As a core component, the spindle must rotate accurately along its intended axis to maintain the integrity of the machining process. However, the spindle may deviate from its ideal path due to various factors, resulting in a runout. Understanding the nature, types, and potential effects of spindle runout is essential to maintaining machining accuracy and extending the life of tools and spindles.
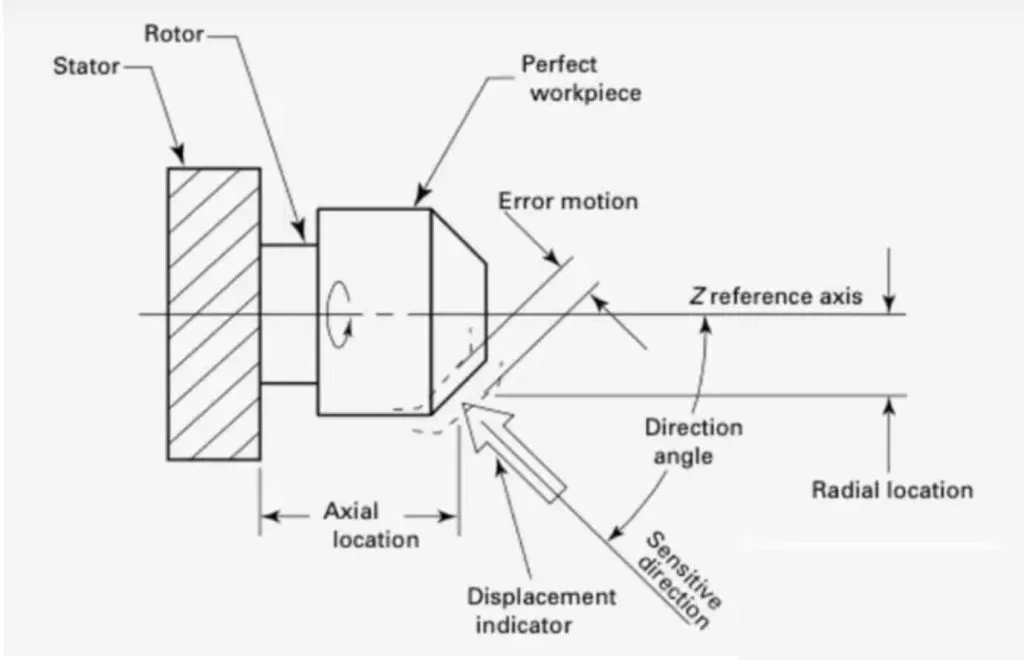
What is a spindle runout?
Spindle runout refers to the phenomenon that the spindle deviates from its intended axis of rotation. During the machining process, this inaccuracy may cause the tool or equipment to deviate from the ideal axis, leading to problems with tolerance control, poor workpiece surface quality, and tool chatter. If not handled in time, spindle runout will significantly shorten the tool’s life, so it is recommended to test the spindle regularly and make necessary repairs.
Types of spindle runout
There are two primary forms of spindle runout: axial runout and radial runout. Both involve the spindle deviating from its intended axis of rotation, but they occur in different directions and have different effects on the machining process.
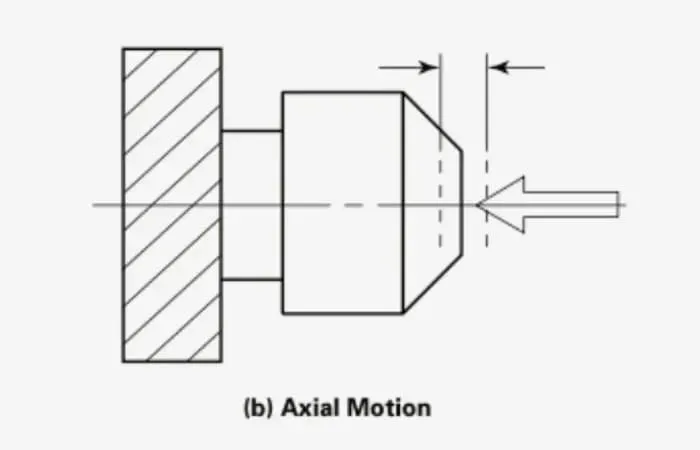

Axial runout
Axial runout is the motion error of a spindle in a direction parallel to its axis of rotation. It refers to the variation in the axial distance between a rotating surface and a reference plane perpendicular to the axis of rotation. Axial runout affects the flatness and parallelism of the machined surface. Axial runout causes a rotating component to move up and down during rotation, resulting in an uneven surface.
Radial runout
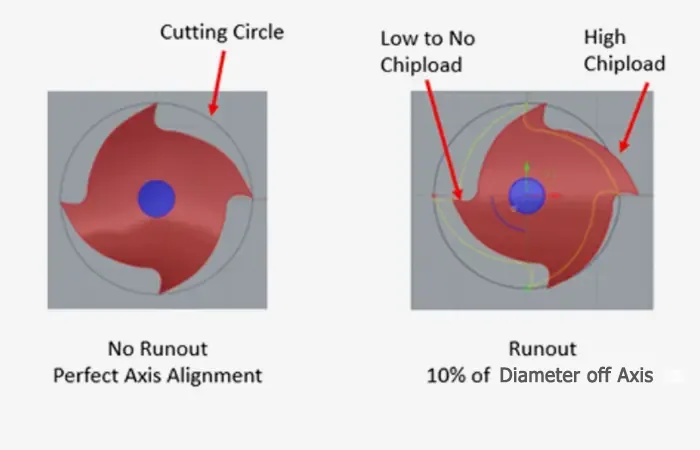
Radial runout is the motion error of a spindle in a direction perpendicular to its axis of rotation. It refers to the variation in the radial distance between the surface of a rotating component and its center axis. Radial runout is usually measured at a specific distance from the axis of rotation and affects the roundness of the machined component. Radial runout causes the rotating surface to move closer to or further away from the center axis as it rotates, resulting in an out-of-round condition.
Effects of spindle runout
Spindle runout can have several adverse effects on the machining process. First, it shortens tool life and increases the likelihood and frequency of part defects. Even if the spindle surface is in good condition if runout is not controlled, spindle life will be shortened, and further damage to the tool and workpiece may occur.
Conclusion
Spindle runout is a critical issue in CNC machining, affecting the quality of machined parts and the life of tools and spindles. By understanding axial and radial runout, operators can better diagnose problems and take corrective actions to ensure machining accuracy. Regular testing and maintenance are essential to minimize the effects of spindle runout and maintain optimal machining performance.
Summary FAQ based on the article
1. What is a spindle runout?
Spindle runout is the phenomenon of the spindle deviating from its intended axis of rotation, resulting in inaccurate machining.
2. What types of spindle runout are there?
The main ones are axial runout (the spindle moves in a direction parallel to the axis) and radial runout (the spindle moves perpendicular to the axis).
3. What effect does spindle runout have on machining?
Spindle runout can cause tolerance control problems, poor workpiece surface quality, tool chatter, and shortened tool life.
4. Why is it essential to test spindle runout regularly?
Regular testing can identify and correct runouts, prevent spindle and tool damage, and ensure machining accuracy.
- RicoCNC has a team of professionals who have been engaged in the design, production, sales, and maintenance of electro spindles for many years. Our company accepts the purchase of various types of CNC spindles.
water-cooled CNC spindle motors
Edge banding machine spindle motors.
- If you need any CNC spindle, please contact us.

